|
Size: 1848
Comment:
|
Size: 1854
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| = Celiac Disease: Incidence and Causes = | '''Celiac Disease: Incidence and Causes''' |
| Line 10: | Line 11: |
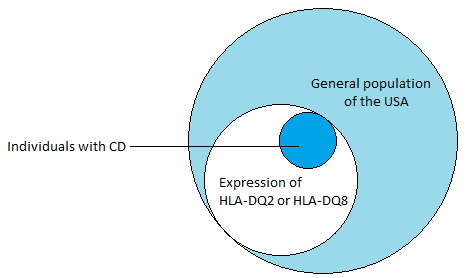
| ||<tablebgcolor="#eeeeee" tablestyle="float:center;font-size:0.85em;margin:0 0 0 0; "style="padding:0.5em; ;text-align:center"> {{attachment:HLA-DQ.png|pop-up text}} <<BR>>'''Fig 1.'''<<BR>>''HLA-DQ alleles are common in the population, this suggest that environmental factors must also play a role in the triggering of CD. Some examples of these environmental factors could be surgery, pregnancy, viral infection or severe emotional stress.'' || | ||<tablebgcolor="#eeeeee" tablestyle="float:center;font-size:0.85em;margin:0 0 0 0; "style="padding:0.5em; ;text-align:center"> {{attachment:HLA-DQ.png|pop-up text}} <<BR>>'''Fig 1.'''<<BR>>''HLA-DQ alleles are common in the population, this suggest that environmental factors must also play a role in the triggering of CD. Some examples of these environmental factors could be surgery, pregnancy, viral infection or severe emotional stress.'' || |
Celiac Disease: Incidence and Causes
Celiac Disease, hereby CD, is a disease that is triggered by the ingestion of gluten (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). It results in a disorder in the small intestine due to an inflammatory reaction to the gluten molecule (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). Approximately 1 % of the European and USAs population suffers from CD (Guandalini et al., 2014). The name celiac derives from the Greek "koiliakos", meaning "belly" (Woodward, 2010). Only 10% to 15% of this affected population have been diagnosed and treated (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). There is a wide array of clinical signs for celiac disease, many of them are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract and this may therefore delay the diagnosis (Kagnoff, 2012). This is a disease that can affect people in any age and the treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Gastrointestinal tract
The primary reaction is the inflammation and damage of the small intestine and as a result the absorbance of important nutrients such as iron, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, proteins, fats and fat-soluble vitamins suffers. This causes secondary reactions as anemia, osteoporosis and abnormal bleeding. Celiac disease is frequently found together with other autoimmune diseases, for exam....
|