|
Size: 1856
Comment:
|
Size: 2640
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| Celiac Disease, hereby CD, is a disease that is triggered by the ingestion of gluten (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). It results in a disorder in the small intestine due to an inflammatory reaction to the gluten molecule (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). Approximately 1 % of the European and USAs population suffers from CD (Guandalini et al., 2014). The name celiac derives from the Greek "koiliakos", meaning "belly" (Woodward, 2010). Only 10% to 15% of this affected population have been diagnosed and treated (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). There is a wide array of clinical signs for celiac disease, many of them are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract and this may therefore delay the diagnosis (Kagnoff, 2012). This is a disease that can affect people in any age and the treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet. | Celiac Disease, hereby '''CD''', is a disease that is triggered by the ingestion of gluten (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). It results in a disorder in the small intestine due to an inflammatory reaction to the gluten molecule (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). Approximately 1 % of the European and USAs population suffers from CD (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). The name celiac derives from the Greek "koiliakos", meaning "belly" (Woodward, 2010). Only 10% to 15% of this affected population have been diagnosed and treated (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). There is a wide array of clinical signs for celiac disease, many of them are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract and this may therefore delay the diagnosis (Kagnoff, 2012). This is a disease that can affect people in any age and the treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet. |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
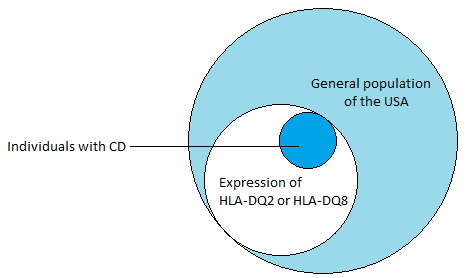
| The primary reaction is the inflammation and damage of the small intestine and as a result the absorbance of important nutrients such as iron, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, proteins, fats and fat-soluble vitamins suffers. This causes secondary reactions as anemia, osteoporosis and abnormal bleeding. Celiac disease is frequently found together with other autoimmune diseases, for exam.... ||<tablebgcolor="#eeeeee" tablestyle="float:center;font-size:0.85em;margin:0 0 0 0; "style="padding:0.5em; ;text-align:center"> {{attachment:HLA-DQ.png|pop-up text}} <<BR>>'''Fig 1.'''<<BR>>''HLA-DQ alleles are common in the population, this suggest that environmental factors must also play a role in the triggering of CD. Some examples of these environmental factors could be surgery, pregnancy, viral infection or severe emotional stress.'' || |
== Extra-intestinal manifestations == = What causes Celiac Disease? = == Pathogenesis == == Diagnosis == = Treatment = == Animal Models == = The prevalence of celiac disease = == General prevalence == == Demographics == == The rising prevalence of Celiac disease == = Discussion = == Gender & ethnic differences == = Conclusion = = References = The primary reaction is the inflammation and damage of the small intestine and as a result the absorbance of important nutrients such as iron, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, proteins, fats and fat-soluble vitamins suffers. This causes secondary reactions as anemia, osteoporosis and abnormal bleeding. Celiac disease is frequently found together with other autoimmune diseases, for example type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis and autoimmune alopecia (Schuppan, et al., 2009). Physicians should be aware for atypical cases, so as to improve diagnosis and avoid complications (Ciclitira, et al., 2005; Mouterde, et al., 2013). Symptoms mainly manifest themselves in the gastrointestinal tract, but there are many extra-intestinal symptoms too. |
| Line 14: | Line 28: |
||<tablebgcolor="#eeeeee" tablestyle="float:center;font-size:0.85em;margin:0 0 0 0; "style="padding:0.5em; ;text-align:center"> {{attachment:HLA-DQ.png|pop-up text}} <<BR>>'''Fig 1.'''<<BR>>''HLA-DQ alleles are common in the population, this suggest that environmental factors must also play a role in the triggering of CD. Some examples of these environmental factors could be surgery, pregnancy, viral infection or severe emotional stress.'' || |
Celiac Disease: Incidence and Causes
Celiac Disease, hereby CD, is a disease that is triggered by the ingestion of gluten (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). It results in a disorder in the small intestine due to an inflammatory reaction to the gluten molecule (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). Approximately 1 % of the European and USAs population suffers from CD (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). The name celiac derives from the Greek "koiliakos", meaning "belly" (Woodward, 2010). Only 10% to 15% of this affected population have been diagnosed and treated (Guandalini & Assiri, 2014). There is a wide array of clinical signs for celiac disease, many of them are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract and this may therefore delay the diagnosis (Kagnoff, 2012). This is a disease that can affect people in any age and the treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Gastrointestinal tract
Extra-intestinal manifestations
What causes Celiac Disease?
Pathogenesis
Diagnosis
Treatment
Animal Models
The prevalence of celiac disease
General prevalence
Demographics
The rising prevalence of Celiac disease
Discussion
Gender & ethnic differences
Conclusion
References
The primary reaction is the inflammation and damage of the small intestine and as a result the absorbance of important nutrients such as iron, folate, vitamin B12, calcium, proteins, fats and fat-soluble vitamins suffers. This causes secondary reactions as anemia, osteoporosis and abnormal bleeding. Celiac disease is frequently found together with other autoimmune diseases, for example type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis and autoimmune alopecia (Schuppan, et al., 2009). Physicians should be aware for atypical cases, so as to improve diagnosis and avoid complications (Ciclitira, et al., 2005; Mouterde, et al., 2013). Symptoms mainly manifest themselves in the gastrointestinal tract, but there are many extra-intestinal symptoms too.
|